The UrbanAir application supports assessing and forecasting air quality in complex urban environments. It is a 3D multiscale model that combines a numerical weather prediction (NWP) model, running at larger scale (e.g. mesoscale), with a city-scale geophysical flow solver for accurate prediction of contaminant transportation through the street corridors, over buildings and obstacles. In particular, the application demonstrates how heavy traffic and poor domestic heat appliances decreases air quality when tight street corridors prevent efficient ventilation. The UrbanAir supports also urban planning when it comes to re-routing road traffic or plan new investments with respect to air quality.
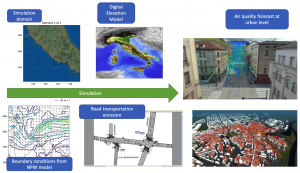
Figure 1 Overview of the UrbanAir application
The key problem in providing accurate forecasts is the lack of complete, well-known emission sources. Taking road transportation as an example, there is a set of parameters that need to be estimated: these include the ratio of cars using gasoline to diesel fuel, fuel usage, emission index, percentage of cars that cold-started, etc. Through the use of computational ensemble simulations, we can address these issues. The VECMAtk automates samples (called ensemble) generation, execution of UrbanAir, collating the results and analyzing them (uncertainty quantification). This simplifies the provision of better prediction results, because many initial conditions with different values are analyzed, to provide mean results (or some weighted ones). Additionally, sensitivity analysis is provided to study the importance of sampled input parameters. Last but not least, the verification and validation techniques deliver the results even more accurate.
